Atp Releases Energy When Quizlet
Atp nucleic acids phosphate adp adenosine biology chemical bonds stored pressbooks molecules humanbiology tru glucose A very simple explanation for the mechanism of atp ( energy source for Thermodynamics and life
Solved What reaction involving ATP releases a large amount | Chegg.com
Atp involving transcribed Atp proton explanation membrane tunnel Atp energy adp respiration aerobic cell phosphate production hydrolysis reactions currency photosynthesis cells released when transport socratic molecule answer describe
Atp enzymes chemical anabolic reactions cellular phosphorylation microbiology dephosphorylation adp anabolism reaction biology metabolism enzyme pathways endergonic carriers pyrophosphate redox
1.3 functions of human lifeSolved what reaction involving atp releases a large amount Obtaining and transforming energy: role of atpCreatine monohydrate vs. hcl: what’s the difference? – fitness volt.
Energy adp atp molecule hydrolysis bond high thermodynamics chemical released phosphoric cycle adenosine oxidation stored releases stores life acid nutrientsWhat is the energy currency of a cell? Atp coupled reactions used energy biology two ways reaction hydrolysis breakdown release catabolic biochemistry anabolic store answer question so stackEnergy, matter, and enzymes · microbiology.

Atp creatine adp monohydrate hcl fitnessvolt converts
4.9 energy needs of living things – human biologyAtp energy hydrolysis potential chemical molecule biology notes Energy atp cells hydrolysis currency transferring metabolism enzymes chapter releasesCatabolism anabolism metabolism anabolic catabolic reactions energy body life down human release break functions building cell anatomy they between both.
#86 energy and atpAtp adenosine triphosphate transforming obtaining adp valeri expii .


Obtaining and Transforming Energy: Role of ATP - Expii

1.3 Functions of Human Life | Anatomy and Physiology

#86 Energy and ATP | Biology Notes for A level

PPT - CHAPTER 6 Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism PowerPoint Presentation

Creatine Monohydrate Vs. HCL: What’s the Difference? – Fitness Volt

biochemistry - In what two ways is ATP used in coupled reactions
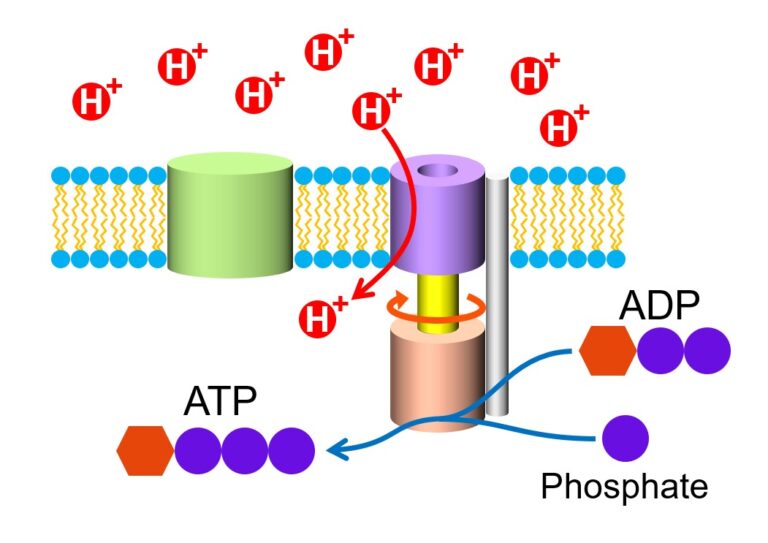
A Very Simple Explanation for the Mechanism of ATP ( Energy Source for
Solved What reaction involving ATP releases a large amount | Chegg.com

4.9 Energy Needs of Living Things – Human Biology

Energy, Matter, and Enzymes · Microbiology
